Kubnernetes and GKE Basics
(This is work in progress...based on GKE docs and some quiklabs)
- Kubernetes only manages nodes - the nodes can be anything (VMs with Kubelet and Kube-Proxy installed)
- Kubernetes itself does not create nodes. GKE Does. And GKE helps with the management.
- Cluster admins create nodes
PODS - Share a common address space
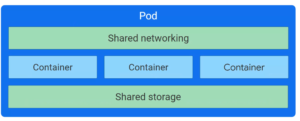
The Control Plane
Kubectl (user types in commands) just calls the API Server
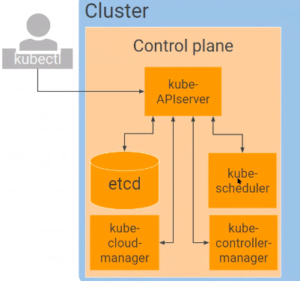
Etcd - A distributed configuration system
- For managing multiple control planes (e.g. production systems).
- Replicates configuration changes from one control plane to others
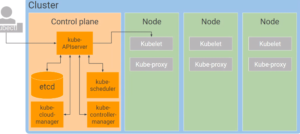
Nodes - Each node contains Kubelet and Kube-proxy
Node Affinity and Node Selectors
Like Labels
Only Launch me if you find a NODE with matching attributes
kind:pod
metadata: node-with-affinity
spec:
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIngoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: accelerator-type
operator: In
values:
- gpu
- tpu
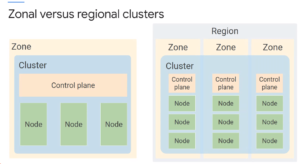
Zonal versus Regional Clusters in GKE
How many Pods and How many Containers in a cluster?
15000 NODES allowed (but 5000 in the context of autoscaling)
Autoscaling Cluster
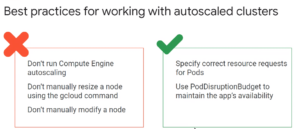
gCloud based Autoscaling of Cluster and Node Pool

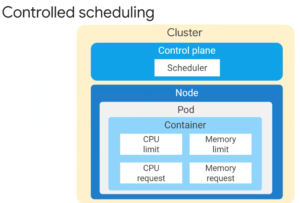
Controlled Scheduling of Nodes in a Cluster
Deployments
- Are stateless
- Deployment object
- Deployment controller
- Uses a Replica Set
- States - Progressing, Complete, Deployed
Rolling Update Deployments (to maintain Availability) versus Recreate (delete and recreate everything without rolling)
- Take place with zero downtime by incrementally updating Pods instances with new ones.
- max unavailable
- max surge
Rolling back a deployment
kubectl rollout undo deployment DEPLOYMENT kubectl rollout undo deployment DEPLOYMENT --to-revision=2 kubectl rollout history deployment DEPLOYMENT --revision=2 --> History
PODS = Container for multiple containers
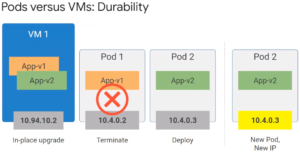
Pods versus VMs - Durability
Pod Conditions that prevent node deletion
- Not run by a controller
- Has local storage
- Restricted by constraint rules
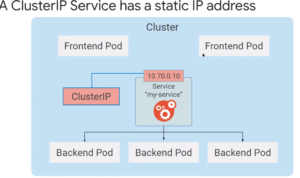
Service - Stable Network Representation of a set of Pods
Introduces stable IP address for Pods (Pod IPs are ephemeral)
Has it's own DNS that produces virtual static IP addresses
Front End Pod -> Back End Pods (also known as Endpoints of the service)
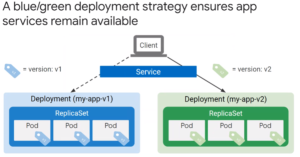
Good for blue green deployment and also Canary Deployment (Gradual percentage of traffic shifting)
Ways to find a service
Environment Variable (service discovery) - Not recommended
Kubernetes has it's own DNS Server - A Record and SRV (Service) Record - for each Service DNS Entry
Istio (Service Mesh) - helps discover other services
Cluster to Cluster Service Discovery?
Istio again. Istio has a Cluser IP Service
ClusterIP Service?
kind: service
metadata:
name: my-service
spec
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: Backend
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 3306
targetPort: 6000
What is a NodePort Service?
The static IP in a ClusterIP service is only visible internally.
For the ClusterIP Static IP to be visible externally, the IP Address is visible to external consumers
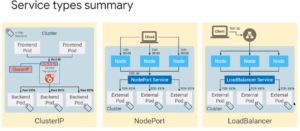
Types of Services in GKE (Load Balancer, Cluster IP)
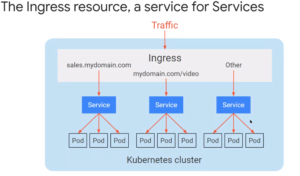
The Ingress Service in GKE
Services for Blue Green (and Canary) Deployments?
Ingress Running on GCP Supports GCP Services
- IAP
- Cloud Armor
- Cloud CDN
Ingress supports gRPC and HTTP2
Container Native Load Balancing
- Network Endpoint Group
- Traffic is appropriately directed
- Support for LB features - IAP, CloudArmor
Network Policies (Pod Level Firewall)
- Need to enable this before you create your cluster
- A pod level FW restricting access to Pods and Services
- Requires at least 2 nodes of n1-standard--1 or higher
- Requires nodes to be recreated
Persistence of Storage
Volumes (emptyDir), configDir, Secrets
Object Kinds
Kind: PersistentVolume versus
Kind: StorageClass
Jobs - Kubernetes
E.g. Transcoding Video Files
completions: --> Number of times you execute the job
Job termination and clean up
backofflimit
DELETE a Job
kubectl delete -f [JOB_FILE]
kubectl delete job [JOB_NAME]
CronJobs - Kubernetes
apiVersion: batch/v1 kind: CronJob metadata:my-app-job name: my-app-job spec: schedule: jobtemplate spec:
Kubeclt Commands
kubectl exec -it POD_NAME - (Interactive )
General Format - Kubeclt exec POD_NAME -- COMMAND - Non Interactive
Main Commands
- kubectl get
- kubectl describe
- kubectk exec
- kubectl logs POD_NAME
kubectl exec democontainer -- ls kubectl apply -f [yaml_deployment_file] - The Apply Command kubectl get deployment (will get all deployments) kubectl describe deployment DEPLOYMENT_NAME - detailed info on running containers
kubectl scale deployment DEPLOYMENT_NAME --replicas=5 Autoscaling - horizontal pod and kubectl autoscale deployment DEPLOYMENT_NAME --min=5 --max=15 --cpu-percent=75 --> horizontal pod autoscaler Update a Deployment kubectl apply - f kubectl set image deployment DEPLOYMENT_NAME IMAGE image:tag kubectl edit \ deployment/DEPLOYMENT_NAME
Example - Deploying 3 Ngnix containers (Reverse Proxy) - and have them up all the time
Leave a Reply